As an important platform compound, furfural can be derived from hemicellulose and further produce non-petroleum derivatives by catalytic hydrogenation process. Nowadays, the highly active catalysts for furfural hydrogenation mainly include noble metals such as Ir, Pt, Rd and their alloys with transition metals. However, considering its economy and the need of industrial production, the research focus of selective hydrogenation of furfural has gradually shifted to the development of transition metal-based catalysts. At the same time, hydrogen molecules are generally used as hydrogen sources in traditional hydrogenation reactions. The production and supply of H2 depend strictly on the exploitation of fossil energy. Moreover, the utilization of hydrogen molecules is low with high energy consumption under harsh conditions. The economic and molecular utilization of hydrogenation reactions need to be improved urgently.
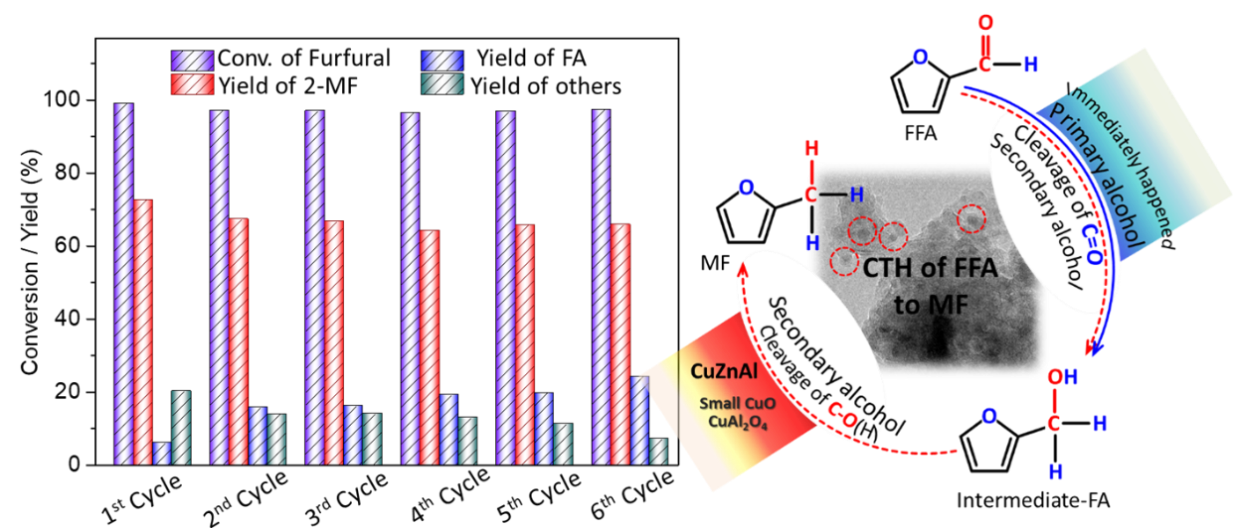
Recently, Professor Liang Changhai and his group used transition metal-based CuZnAl catalysts to prepare 2-methylfuran by catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural with alcohols as hydrogen donors under atmospheric pressure. CuZnAl catalyst exhibits excellent hydrogen dissociation performance, 2-methylfuran selectivity and stability. The results show that secondary alcohols such as isopropanol as solvents and hydrogen sources can effectively avoid the side reactions such as decarbonylation and furan ring hydrogenation. At the same time, the presence of CuO and CuAl2O4 crystals in the precursor of CuZnAl catalyst is beneficial to improve the redox and hydrogen dissociation properties.

In addition, the synergistic effect of Cu-Zn species can effectively regulate the product distribution. When the atomic ratio of Cu/Zn is 2.5:1, 99% conversion of furfural reaches and the 72% yield of 2-methylfuran can be achieved at 180 oC in N2 4 hours. After six cycles, the conversion of furfural and the yield of 2-methylfuran remain basically stable. The related work provides a possibility for the application of green and low-cost CuZnAl catalyst in furfural production of 2-methylfuran and furan industry.
The work has been published on the journal of Industrial Engineering & Chemistry Research (2019, 16, 6298-6308) as the supplementary cover. This is also one of the articles presented by the Lab of Advanced Materials & Catalytic Engineering for the 70th Anniversary of Dalian University of Technology!
Article link: