Recently, important research achievements in catalytic hydrodesulfurization by using transition metal silicides has been obtained. The results were published in the Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 369, 363-371, entitled "A highly efficient and sulfur-tolerant Pd2Si/CNTs catalyst for hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophenes".
Researchers in AM&CE has carried out in-depth studied on the controllable preparation and catalytic performance of transition metal silicide nanomaterials. A variety of bulk and supported nano-silicide catalysts, such as cobalt silicide, iron silicide, nickel silicide and manganese silicide, were prepared by metal organic chemical vapor deposition, temperature programmed silicification and dual-source precursor pyrolysis. The prepared metal silicide nanomaterials exhibit good properties in selective hydrogenation, hydrodesulfurization, methanation and magnetic properties. Relevant research results have published nearly 30 related research papers and authorized 3 Chinese invention patents.
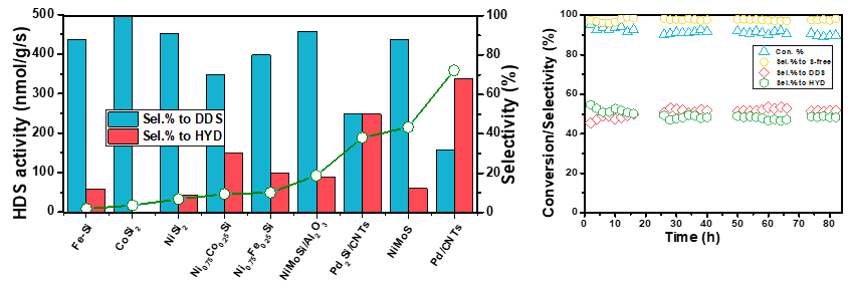
Previously, the hydrodesulfurization performance of nickel silicide was systematically studied by theoretical calculation and experimental method. The results show that the covalent interaction between Si and Ni completely changed the electronic structure of Ni surface, thus showing high hydrodesulfurization activity and high sulfur resistance, which is completely different from transition metal nitrides, carbides or phosphides (RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 1728). We also synthesized cobalt-nickel oxide and iron-nickel oxide solid solution by coprecipitation of polyols, and nickel-based bimetallic silicides with different cobalt-nickel ratio and iron-nickel ratio by temperature programmed silicification of SiH4/H2. The results show that bimetallic silicides have higher hydrodesulfurization activity than single metal silicides, and a small amount of Co(Fe) doping significantly improves their hydrodesulfurization activity (J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 24968 and J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 29052).
Article link: